
The international conference ACM SenSys 2025, which took place on May 6-9 in Irvine (USA), was one of the key scientific events devoted to sensor systems and their applications in industry, medicine, engineering and intelligent systems.


The event gathered hundreds of researchers, engineers and industry representatives from around the world. The program included numerous plenary sessions, workshops and poster sessions, which presented the latest achievements in areas such as the Internet of Things, wearable systems, sensors in medicine and industry, as well as modern data processing methods.

We are pleased to announce that our research group presented five significant works that were highly rated by participants and reviewers.
Our articles and research results presented
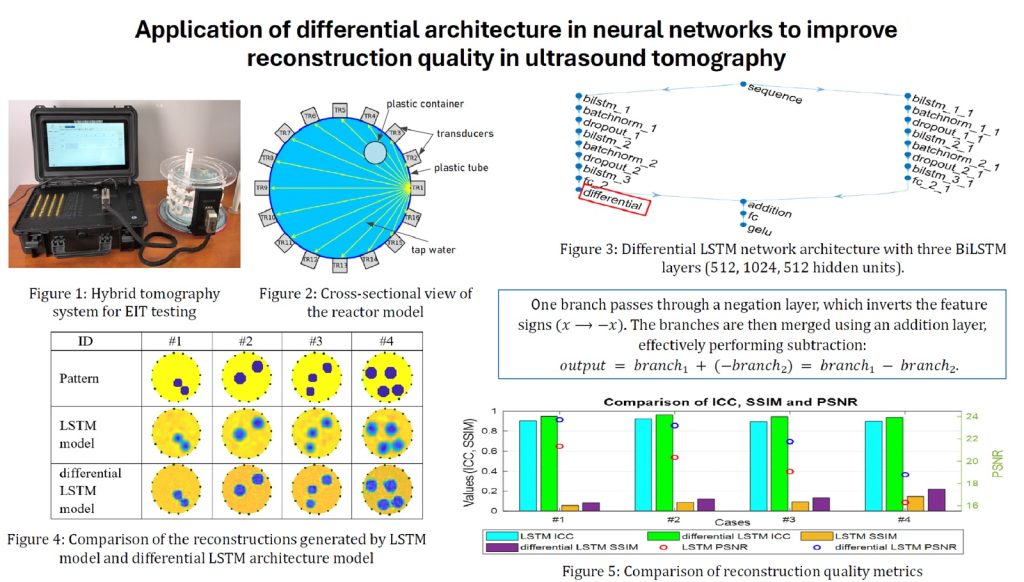
The first paper, entitled “Application of differential architecture in neural networks to improve reconstruction quality in ultrasound tomography” (authors: Monika Kulisz, Grzegorz Kłosowski, Tomasz Rymarczyk, Konrad Niderla, Paweł Olszewski, Dariusz Wójcik), concerned an innovative approach using a two-track differential architecture based on an LSTM network. The aim was to improve the quality of images in industrial ultrasound tomography. The proposed architecture allows for better capturing of residual components, which translates into improved sharpness, accuracy and clarity of tomographic images. The results of experiments, conducted using a 16-transducer system, showed the advantage of the differential method over standard solutions, achieving higher PSNR and SSIM indices.
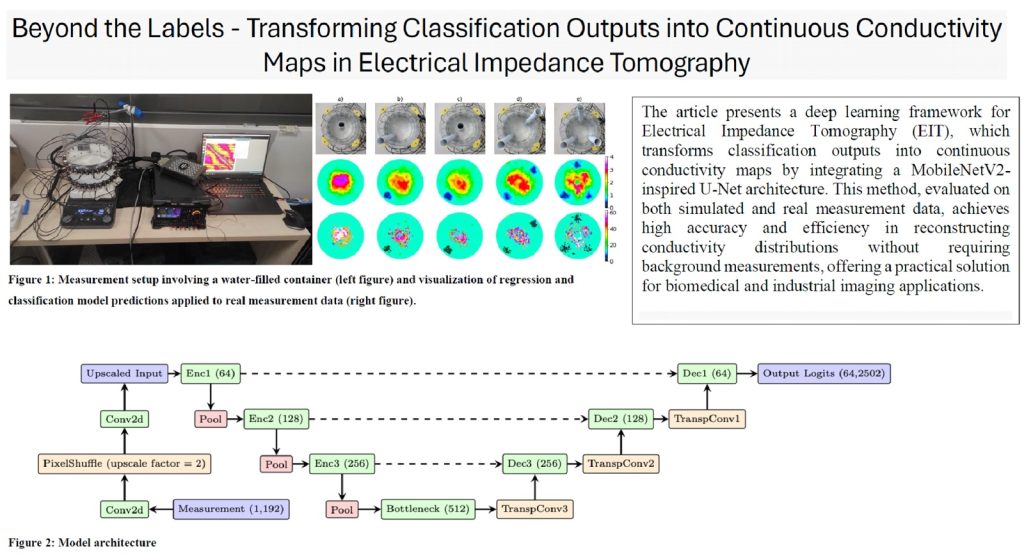
The next publication, “Beyond labels – transformation of classification results into continuous conductivity maps in impedance tomography” (authors: Dariusz Wójcik, Dariusz Majerek, Tomasz Rymarczyk, Tomasz Łobodiuk, Michał Oleszek, Krzysztof Król), presented a hybrid model based on the U-Net architecture with MobileNetV2 blocks. This model is used to reconstruct continuous conductivity maps based on classification. It integrates regression with classification, transforming class probabilities into conductivity values by applying appropriate weights. This approach enables effective reconstruction of conductivity maps without the need to perform reference measurements, which is crucial in industrial and biomedical applications.

The third article, “Three-dimensional acoustic beam defectoscope in industrial applications” (authors: Michał Gołąbek, Barbara Stefaniak, Dariusz Wójcik, Tomasz Rymarczyk), described a modern diagnostic system developed by the team. It uses beamforming technology, which enables precise detection of defects in industrial structures. The device supports three-dimensional reconstruction of detected anomalies, offering high resolution and better visualization quality than solutions available on the market. In the conducted tests, the new technology showed a significant advantage in parameters such as MSE, PSNR and SSIM, which confirms its effectiveness in industrial applications.
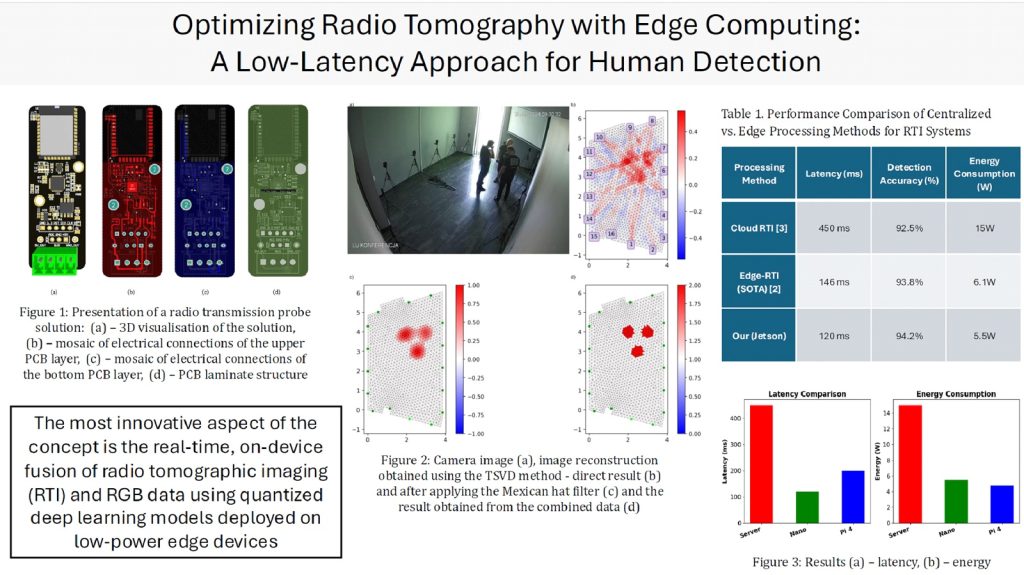
The fourth paper, “Optimization of radio-tomography using edge computing: low-latency approach to human presence detection” (authors: Michał Maj, Tomasz Rymarczyk, Michał Styła, Tomasz Cieplak, Damian Pliszczuk, Jakub Pizoń), presented an innovative solution combining radio-tomography data and RGB image. This data is processed directly on edge devices such as Jetson Nano and Raspberry Pi. The system achieved significant reduction of latency (up to 120 ms) and power consumption (5.5 W), while improving detection accuracy (94.2%). This paper opens new possibilities for implementing energy-efficient and privacy-friendly solutions for human presence monitoring in smart buildings and security systems.
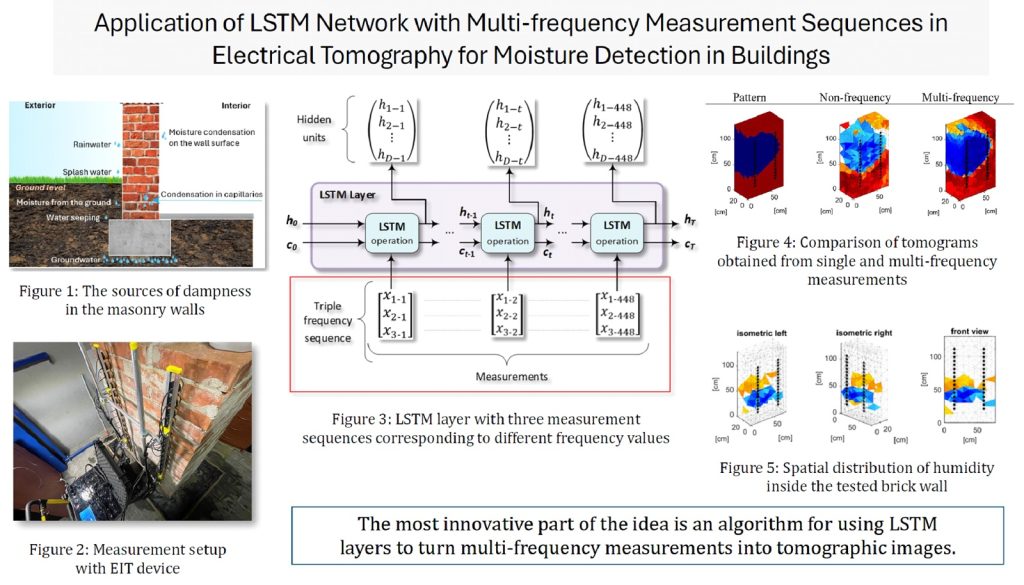
The last of the presented works is “Application of LSTM network with multi-frequency measurement sequences in impedance tomography for moisture detection in buildings” (authors: Grzegorz Kłosowski, Tomasz Rymarczyk, Monika Kulisz, Michał Oleszek, Konrad Niderla). It presents an innovative algorithm using multi-frequency measurement sequences processed by LSTM network to improve the quality of moisture imaging in building walls. Studies have shown that this approach significantly improves the resolution and accuracy of images in comparison to single-frequency methods. This may contribute to the popularization of this method in the conservation of monuments and general construction.

The presence and active participation of the research team at one of the most important sensor conferences in the world underlines the importance of the work carried out for the scientific and industrial community.

The presented results were appreciated by the participants of the event, confirming the high quality and practical potential of the developed solutions. In particular, it is worth emphasizing the interdisciplinarity of the topics discussed, which combine advanced machine learning methods, modern measurement technologies and real applications in industry, medicine and construction.

