The 34th Symposium on Applications of Electromagnetism took place in Jaroszowice, presenting innovations in engineering and medicine
On June 8-11, 2025, the 34th PTZE Symposium entitled “Applications of Electromagnetism in Modern Engineering and Medicine” was held in Jaroszowice. The conference brought together a diverse group of scientists, engineers and medical specialists to present and discuss the latest achievements in the field of electromagnetism applications. The event was co-organized by the Polish Society for the Application of Electromagnetism, the Netrix S.A. Research and Development Center and several leading Polish universities.

The conference program covered a wide range of topics, from bioelectromagnetism and electromagnetic materials to advanced computational methods and industrial tomography. The symposium structure, combining plenary, oral and poster sessions, encouraged lively discussions and the establishment of scientific cooperation.
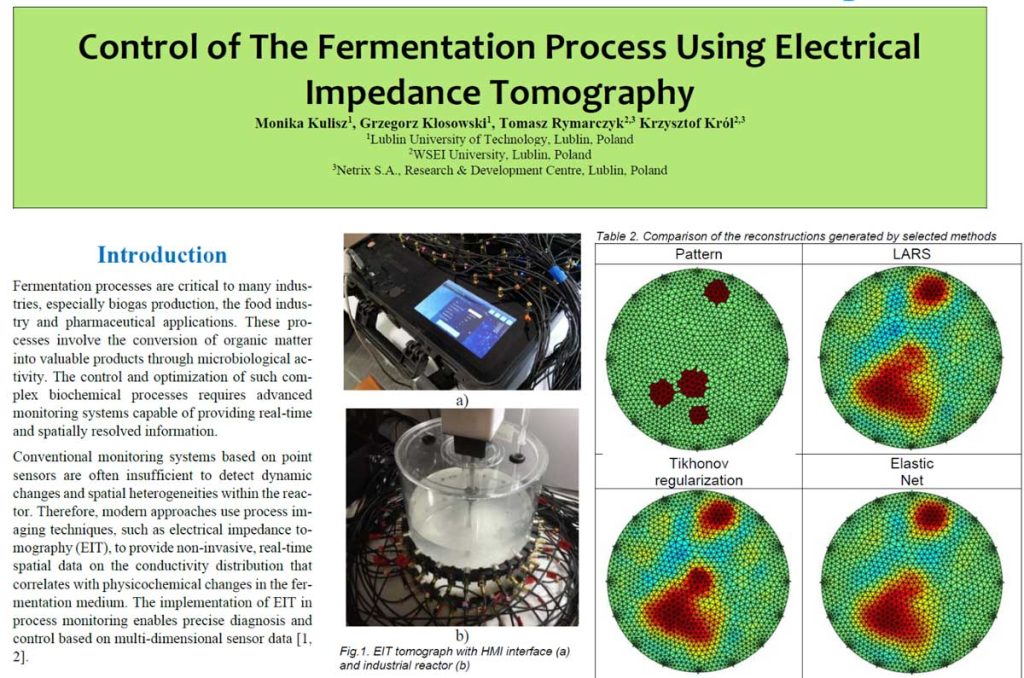
During the conference, the trend of developing advanced imaging techniques was clearly visible. Innovative tomography systems were presented, which are used in both medical diagnostics and industry. Scientists presented solutions using electrical impedance tomography to monitor lung diseases and ultrasound tomography, including wearable systems for continuous monitoring of the lower urinary tract. At the same time, industrial flaw detectors based on beam shaping technology were shown, which enable precise, non-destructive testing of materials and detection of internal defects. The development of these methods is strongly supported by advanced image reconstruction algorithms, which increase their accuracy and reliability.

Another dominant theme was the integration of artificial intelligence and machine learning with electromagnetic systems. Many of the solutions presented used AI algorithms to optimize device performance and data analysis. Examples included the use of knowledge distillation to create fast and efficient AI models for embedded systems, capable of recognizing emotions from images and sounds. Other researchers focused on the use of evolutionary algorithms to train recurrent neural networks for industrial process control and machine load prediction. Machine learning also proved crucial in improving the accuracy of indoor location systems based on ultra-wideband (UWB) technology.

The symposium was also a platform for presenting innovations in sensor technology and the Internet of Things (IoT). New hardware solutions for non-invasive health monitoring were developed, integrating spectral impedance technology for glucose measurement with optical sensors for heart rate and blood oxygen saturation analysis. Miniaturized, multi-functional UWB tags were also presented, which, in addition to precise location, offer the possibility of monitoring environmental conditions, making them a versatile IoT platform for logistics and smart warehouses.
Conference participants could also learn about the growing importance of virtual and digital twin technologies in industrial applications. Of particular interest was the presentation of the “Tomoverse” platform, which enables the management of virtual space for the implementation of scenarios using ultrasonic tomography. This system integrates data from real processes with numerical simulations and interactive 3D environments, creating coherent digital twins that support remote collaboration, training and optimization of industrial processes.

The Symposium in Jaroszowice confirmed once again that the applications of electromagnetism are a dynamically developing, interdisciplinary field that plays a key role in technological progress in medicine and engineering.

